Eggs are a powerhouse of nutrition, boasting a rich array of proteins that are essential for human health. These versatile foods are not only a staple in many diets around the world but also a subject of scientific interest due to their high protein content. Understanding the protein content of eggs can help individuals make informed dietary choices, especially those seeking to increase their protein intake for fitness, weight loss, or muscle-building purposes.
The protein content of eggs is one of their most celebrated features, offering a complete amino acid profile that is crucial for various bodily functions. Whether consumed as a breakfast staple, a post-workout snack, or a key ingredient in numerous recipes, eggs provide an excellent source of protein that supports muscle repair, immune function, and overall health. But how much protein does an egg actually contain, and what makes it such a valuable source of nutrition?
In this article, we delve into the protein content of eggs, exploring their nutritional benefits, comparing them with other protein sources, and examining how eggs can be incorporated into a balanced diet. From understanding the different types of protein in eggs to addressing common questions about egg consumption, this comprehensive guide aims to shed light on why eggs are considered a nutritional powerhouse.
Table of Contents
- What is the Protein Content of Eggs?
- How Do Eggs Compare to Other Protein Sources?
- Why Are Eggs a Complete Protein?
- Health Benefits of Egg Protein
- How Does Cooking Affect the Protein in Eggs?
- Are There Differences in Protein Content Between Egg Types?
- How Much Protein is in an Egg White vs. an Egg Yolk?
- What Role Does Egg Protein Play in Muscle Building?
- Can Eggs Help with Weight Management?
- Is There a Recommended Daily Intake of Egg Protein?
- How to Incorporate Eggs into a Protein-Rich Diet?
- Potential Risks of Consuming Too Many Eggs?
- Are There Alternatives to Egg Protein for Vegans?
- Are Eggs Good for Everyone?
- FAQs about Egg Protein
- Conclusion
What is the Protein Content of Eggs?
Eggs are renowned for their high protein content, making them a favorite among health enthusiasts and fitness gurus. A single large egg contains about 6 grams of protein, which accounts for a significant portion of the daily recommended intake. The protein in eggs is of high quality, containing all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. This makes eggs a "complete protein" source, similar to meat, fish, and dairy.
In addition to the protein content, eggs are also rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin D, B vitamins, selenium, and choline. These nutrients contribute to the overall nutritional value of eggs, supporting various bodily functions such as brain health, bone strength, and immune support. The protein content of eggs is evenly distributed between the egg white and the yolk, although the white contains the majority of the protein.
For individuals seeking to maximize their protein intake, consuming eggs can be an effective strategy. Not only do they provide a substantial amount of protein, but they also offer a low-calorie option compared to other protein-rich foods. This makes eggs an excellent choice for those aiming to build muscle, lose weight, or maintain a balanced diet.
How Do Eggs Compare to Other Protein Sources?
When it comes to protein content, eggs hold their own against other popular protein sources. For instance, a large egg typically contains about 6 grams of protein, which is comparable to a 1-ounce serving of meat or fish. However, eggs have the added advantage of being a complete protein, offering all the essential amino acids required for optimal health.
Compared to plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, or nuts, eggs often have a higher protein density. While plant proteins can be a great addition to a balanced diet, they may lack one or more essential amino acids, requiring careful combination to achieve a complete protein profile. Eggs, on the other hand, provide a convenient and efficient way to meet protein needs without the need for complex meal planning.
In addition to their protein content, eggs are also lower in carbohydrates and fats compared to other protein-rich foods like cheese or nuts. This makes them an ideal choice for individuals following a low-carb or ketogenic diet. Furthermore, the affordability and versatility of eggs make them accessible to a wide range of people, allowing for creative culinary applications that can enhance any meal.
Why Are Eggs a Complete Protein?
The designation of eggs as a "complete protein" stems from their comprehensive amino acid profile. Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of the body's tissues and organs. Of the 20 amino acids that the body uses, nine are considered essential because they cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet. Eggs contain all nine essential amino acids, making them a complete protein source.
This complete protein profile is crucial for various physiological functions, including muscle growth and repair, hormone production, and immune function. The presence of all essential amino acids in eggs means that they can efficiently support these functions without the need for additional protein sources. This is particularly beneficial for individuals looking to optimize their protein intake for fitness or health reasons.
Moreover, the protein in eggs is highly bioavailable, meaning that the body can readily absorb and utilize it. This high bioavailability is attributed to the egg's balanced amino acid composition, which closely matches the body's needs. As a result, the protein content of eggs is not only high in quantity but also in quality, making them a valuable addition to any diet.
Health Benefits of Egg Protein
The protein content of eggs offers numerous health benefits that extend beyond simple muscle building. One of the key advantages of egg protein is its role in supporting weight management. High-protein foods like eggs can increase satiety, reduce hunger, and promote a feeling of fullness, which can help individuals consume fewer calories overall and support weight loss efforts.
Egg protein also plays a vital role in muscle maintenance and repair. For those engaging in regular physical activity, especially strength training or endurance exercises, consuming adequate protein is essential for muscle recovery and growth. Eggs provide a convenient and effective way to meet protein needs post-workout, aiding in muscle repair and reducing recovery time.
Additionally, the protein in eggs supports immune function by providing the necessary building blocks for immune cells. A strong immune system is vital for protecting the body against infections and diseases, and consuming sufficient protein is an important part of maintaining immune health. The presence of other nutrients in eggs, such as vitamin D and selenium, further enhances their immune-boosting properties.
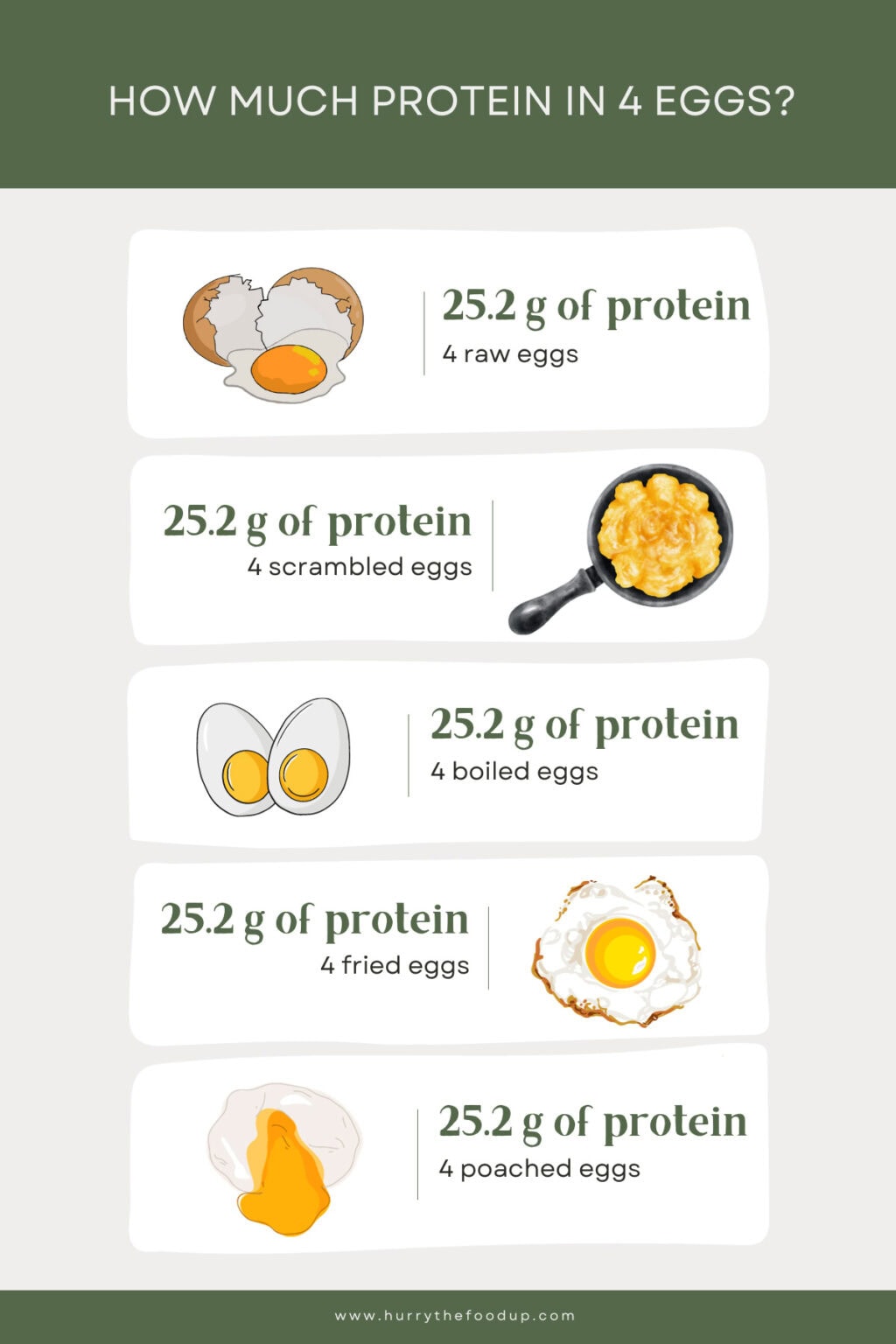
How Does Cooking Affect the Protein in Eggs?
Cooking eggs can impact their protein content and digestibility, but rest assured, the protein remains largely intact. The process of cooking denatures the proteins in eggs, which means that the protein molecules unfold and rearrange. This denaturation is beneficial as it makes the proteins more digestible, allowing the body to absorb and utilize them more efficiently.
Different cooking methods can have varying effects on the protein in eggs. For example, boiling, poaching, or scrambling eggs are considered healthy cooking methods that preserve their nutritional content. Frying eggs, on the other hand, may add additional calories and fats, depending on the amount of oil or butter used. Nonetheless, the protein content remains largely unaffected by the cooking method.
It's also important to note that overcooking eggs can lead to the loss of some nutrients, particularly certain vitamins that are sensitive to heat. To maximize the nutritional benefits of eggs, it's advisable to cook them until the whites are firm and the yolks are still slightly runny, as this helps retain their nutrient content while ensuring food safety.
Are There Differences in Protein Content Between Egg Types?
While the protein content of eggs is generally consistent across different types, there may be slight variations depending on factors such as the hen's diet, breed, and environment. Conventional eggs, organic eggs, free-range eggs, and pasture-raised eggs all provide similar amounts of protein, typically around 6 grams per large egg.
The primary differences between these egg types lie in their production methods and potential nutritional variations in other areas. For instance, eggs from hens fed a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids may contain higher levels of these beneficial fats. However, these differences do not significantly impact the protein content of the eggs.
Consumers may choose different egg types based on personal preferences, ethical considerations, or specific dietary needs. Regardless of the type, eggs remain a highly nutritious and protein-rich food choice that can fit into a variety of dietary patterns.
How Much Protein is in an Egg White vs. an Egg Yolk?
The protein content of an egg is distributed between the egg white and the yolk, with the white containing the majority of the protein. A large egg white contains approximately 3.6 grams of protein, while the yolk contains about 2.7 grams of protein. This distribution makes egg whites a popular choice for those looking to maximize protein intake while minimizing calorie and fat consumption.
While egg whites are rich in protein, the yolk provides additional nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. The yolk contains essential nutrients like vitamin D, choline, and lutein, which contribute to overall health and well-being. Therefore, consuming the whole egg can offer a more balanced and comprehensive nutritional profile.
For individuals with specific dietary goals, such as reducing cholesterol intake, egg whites can be a suitable option. However, for those seeking the full range of nutrients that eggs have to offer, including the yolk in their diet can be beneficial.
What Role Does Egg Protein Play in Muscle Building?
Egg protein is a valuable ally for individuals aiming to build muscle mass and strength. The high-quality protein in eggs contains all the essential amino acids needed for muscle protein synthesis, the process by which the body repairs and builds new muscle tissue. Consuming sufficient protein is crucial for anyone engaged in resistance training, as it supports muscle growth and recovery.
One of the key benefits of egg protein is its bioavailability, which means that the body can efficiently absorb and utilize the amino acids it provides. This makes eggs an excellent post-workout food option, as they deliver the necessary nutrients to the muscles when they need it most. Additionally, the convenience and versatility of eggs make them easy to incorporate into a variety of meals and snacks.
Incorporating eggs into a balanced diet alongside other protein sources can help individuals meet their daily protein needs and support their muscle-building goals. Whether consumed as a standalone snack or included in dishes like omelets, salads, or protein shakes, eggs offer a versatile and effective way to boost protein intake.
Can Eggs Help with Weight Management?
Eggs can play a beneficial role in weight management due to their high protein content and low-calorie profile. Protein is known to increase feelings of fullness and satiety, which can help individuals control their appetite and reduce overall calorie intake. This makes eggs an excellent food choice for those looking to lose or maintain weight.
Studies have shown that consuming eggs for breakfast can lead to greater satiety and reduced calorie consumption throughout the day compared to other breakfast options. This effect is attributed to the protein content of eggs, which helps regulate hunger hormones and stabilize blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, eggs are a versatile food that can be prepared in numerous ways to suit different dietary preferences and meal plans. Whether boiled, scrambled, or poached, eggs can be easily incorporated into a balanced diet that supports weight management goals.
Is There a Recommended Daily Intake of Egg Protein?
While there is no specific recommended daily intake for egg protein, dietary guidelines suggest consuming a variety of protein sources to meet daily protein needs. The amount of protein required varies based on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and health goals. On average, adults are advised to consume 46 to 56 grams of protein per day, with eggs being one of the many options to achieve this target.
Including eggs as part of a balanced diet can contribute to meeting daily protein requirements, providing about 6 grams of protein per large egg. It's important to consider individual dietary needs and preferences when determining the appropriate intake of egg protein.
For individuals with specific health conditions or dietary goals, consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on protein intake and the role of eggs in their diet.
How to Incorporate Eggs into a Protein-Rich Diet?
Incorporating eggs into a protein-rich diet is both easy and versatile, thanks to their culinary flexibility and nutritional benefits. Here are some simple ways to include eggs in your meals:
- Breakfast: Start your day with a protein-packed breakfast by making an omelet with vegetables, cheese, and lean meats. Alternatively, enjoy boiled or poached eggs with whole-grain toast for a balanced meal.
- Snacks: Hard-boiled eggs make for a convenient and portable snack option that can be enjoyed on the go. Pair them with a piece of fruit or a handful of nuts for added nutrition.
- Lunch and Dinner: Add eggs to salads, grain bowls, or stir-fries for an extra protein boost. You can also use eggs as a topping for pizza or incorporate them into casseroles and baked dishes.
- Desserts and Baked Goods: Use eggs in baking recipes to enhance the protein content of desserts like muffins, cakes, and cookies. Eggs can also be included in homemade protein bars or energy bites.
By experimenting with different recipes and cooking methods, you can enjoy the nutritional benefits of eggs while adding variety to your diet.
Potential Risks of Consuming Too Many Eggs?
While eggs are a nutritious and protein-rich food, consuming them in excess may pose certain risks for some individuals. One of the primary concerns is the cholesterol content in egg yolks, which has historically been linked to increased blood cholesterol levels and heart disease risk.
However, recent research suggests that dietary cholesterol from eggs may have a smaller impact on blood cholesterol levels than previously thought, and moderate egg consumption is considered safe for most people. The American Heart Association advises that individuals with normal cholesterol levels can safely consume one egg per day as part of a healthy diet.
For those with specific health conditions, such as hypercholesterolemia or cardiovascular disease, it may be advisable to limit egg consumption and focus on egg whites, which are free of cholesterol. Consulting a healthcare professional can provide personalized recommendations based on individual health status and dietary needs.
Are There Alternatives to Egg Protein for Vegans?
For individuals following a vegan diet, there are several plant-based protein alternatives to eggs that can provide similar nutritional benefits. Some popular options include:
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of plant-based protein and can be used in a variety of dishes, from soups and stews to salads and burgers.
- Tofu and Tempeh: Made from soybeans, tofu and tempeh are versatile protein sources that can be grilled, stir-fried, or added to curries and stir-fries.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide protein and healthy fats, making them great additions to smoothies, oatmeal, or baked goods.
- Quinoa: This nutrient-dense grain is a complete protein source and can be used as a base for salads, bowls, or side dishes.
Incorporating a variety of these plant-based protein sources into a vegan diet can help ensure adequate protein intake and provide a balanced nutritional profile.
Are Eggs Good for Everyone?
Eggs are a nutritious food that can be enjoyed by most people, offering a rich source of protein, vitamins, and minerals. However, individual dietary needs and health conditions may influence whether eggs are a suitable choice for everyone.
For those with egg allergies, consuming eggs can trigger allergic reactions and should be avoided. Additionally, individuals with specific dietary restrictions, such as those following a vegan diet, may choose to exclude eggs from their diet and seek alternative protein sources.
Overall, eggs can be a valuable addition to a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients that support various aspects of health. As with any food, moderation and variety are key to maintaining a healthy and well-rounded diet.
FAQs about Egg Protein
1. How much protein is in a large egg?
A large egg contains approximately 6 grams of protein, making it a substantial source of high-quality protein.
2. Can I eat eggs every day?
For most individuals, consuming one egg per day is considered safe and can be part of a healthy diet. However, those with specific health conditions should consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
3. Is egg protein good for muscle building?
Yes, egg protein is an excellent choice for muscle building due to its complete amino acid profile and high bioavailability, making it effective for muscle repair and growth.
4. How does the protein in egg whites compare to the yolk?
Egg whites contain more protein than the yolk, with approximately 3.6 grams of protein per large egg white compared to 2.7 grams in the yolk.
5. Are eggs suitable for weight loss diets?
Eggs can be beneficial for weight loss diets due to their high protein content, which promotes satiety and helps control appetite.
6. Do eggs contain all the essential amino acids?
Yes, eggs are a complete protein source, containing all nine essential amino acids required for optimal health.
Conclusion
The protein content of eggs makes them a nutritional powerhouse, offering a complete and highly bioavailable source of essential amino acids. Whether consumed as part of a muscle-building plan, a weight management strategy, or a balanced diet, eggs provide a convenient and versatile way to meet protein needs. While individual dietary preferences and health conditions may influence egg consumption, their numerous health benefits make them a valuable addition to many diets. By understanding the protein content and nutritional advantages of eggs, individuals can make informed choices that support their overall health and well-being.
For more information on the benefits of dietary protein, visit the Healthline article on protein benefits.
You Might Also Like
How To Spend $25 On Robux Wisely: A Beginner's GuideMastering The Role: The Dark Knight Rises Bane Actor
Essential Knowledge: What Does A Gallon Of Water Weigh?
Eva Marcille: The Phenomenal Rise Of America's Next Top Model
The Origins Of Ludacris: What High School Did Ludacris Go To?
Article Recommendations